What is shoulder instability?
It concerns the relationship between the head of the humerus and scapula, called articulation “glenohumeral.”
There is talk of instability when a patient presents three types of symptoms on this link: dislocations, subluxations or concerns.
A dislocation is a dislocation of the joint that is given up by a third. We talk about reduction when “réemboite ‘shoulder.
A subluxation is dislocation of the joint that the patient reduces itself spontaneously without using a third party.
Apprehension is the feeling that the shoulder will uncouple. This impression felt by the patient occurs in gestures of greater or lesser magnitude. The patient knows that instability gestures that are unpleasant and ended it by avoiding them.
One or more of these three symptoms may be felt by the patient. They characterize the instability of the shoulder.
Which anatomical lesions are these symptoms of instability?
Elements that stabilize the shoulder are:
- bones: the humerus and the shoulder blade (aka scapula)
- the bead: which is the edge of the articular region of the scapula
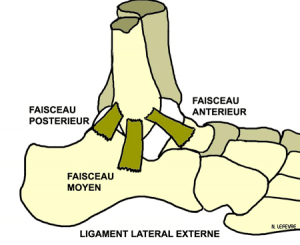
- ligaments: glenohumeral (upper, middle and lower coracohumeral)
- the muscles of the shoulder deltoid, trapezius, rotator cuff (supra and infra supinatus, subscapularis tendon of the biceps, small round), pectoralis
If one or more elements which stabilize the joint is or are reached (s): the shoulder can become unstable. During dislocation episodes, there is always a violation of one or more of these components. Each new episode of dislocation, there is damage to the joint.
What medical imaging examinations used to make the diagnosis?
The complete imaging tests clinical analysis and enable accurate diagnosis.
Is made ??of shoulder radiographs to search for recent or old fractures that indicate that there have been episodes of instability (notch of the humeral head fracture separation or fracture compression of the glenoid).
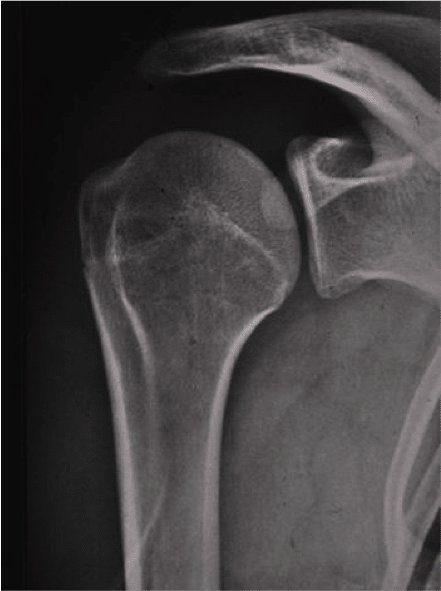
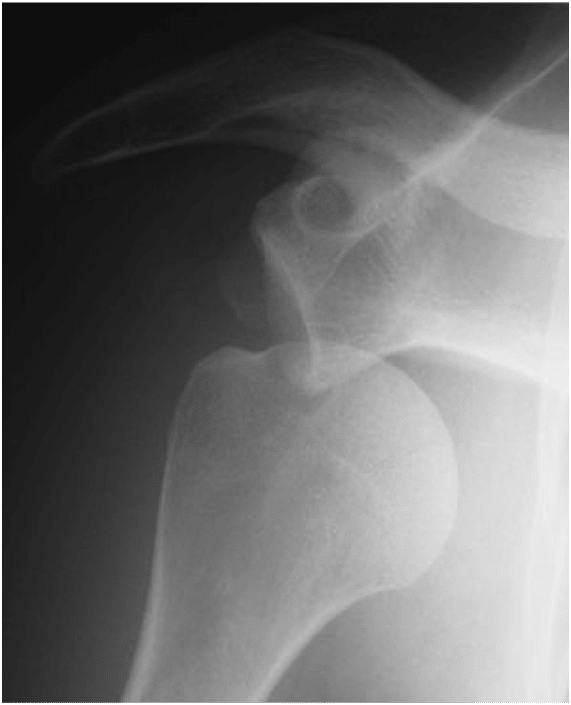
There is provided a shoulder arthrography
This is a product injected into the joint to see negative anomalies of the joint. Ligament injury, bead, cartilage. Is the gold standard for analysis of the lesions in the framework of an instability of the shoulder.Ultrasound does not see the relationship as a whole. MRI visualizes also less precisely the areas concerned.
Not to be confused with laxity of the shoulder
We must differentiate the instability of the so-called laxity
The laxity is not felt by the patient but is what the doctor finds during the examination in consultation.By examining the amplitudes of the joint, the doctor receives an abnormal motion of the humerus relative to the scapula or relative to the other shoulder is compared to the “average” of the normal population.There is talk of laxity if external rotation exceeds 85 °. Hyperlaxe a patient is not necessarily unstable but is laxity factor promoting instability.
Doctor Yoann BOHU, Doctor Nicolas LEFEVRE, Doctor Serge HERMAN. – 1 décembre 2013.